SQL WITH
LESSONS
Want to try your newly developed SQL skills?
Start with WeldEarlier in the tutorial, you learned that the select function could only be used once in a query. This is actually not entirely true — but you need to be careful about how you structure a query to make sure that it returns the desired result. This is how a CTE query is structured:
The first step of the query groups by 'order_id', and the second step aggregates across all the rows. This way it finds the average revenue per order, the smallest order, and the largest order, which it would have not been able to find without aggregating on an order level. You can write this query as follows:
1with
2 value_per_order as (
3 select
4 order_id
5 , sum(quantity * price) total_revenue_per_order
6 from
7 {{raw.e_commerce_sample.webshop_order_line}}
8 group by
9 order_id
10 )
11select
12 sum(total_revenue_per_order) as total_revenue
13 , avg(total_revenue_per_order) as average_revenue_per_order
14 , min(total_revenue_per_order) as smallest_order
15 , max(total_revenue_per_order) as largest_order
16from
17 value_per_order…and the resulting table should look like this:

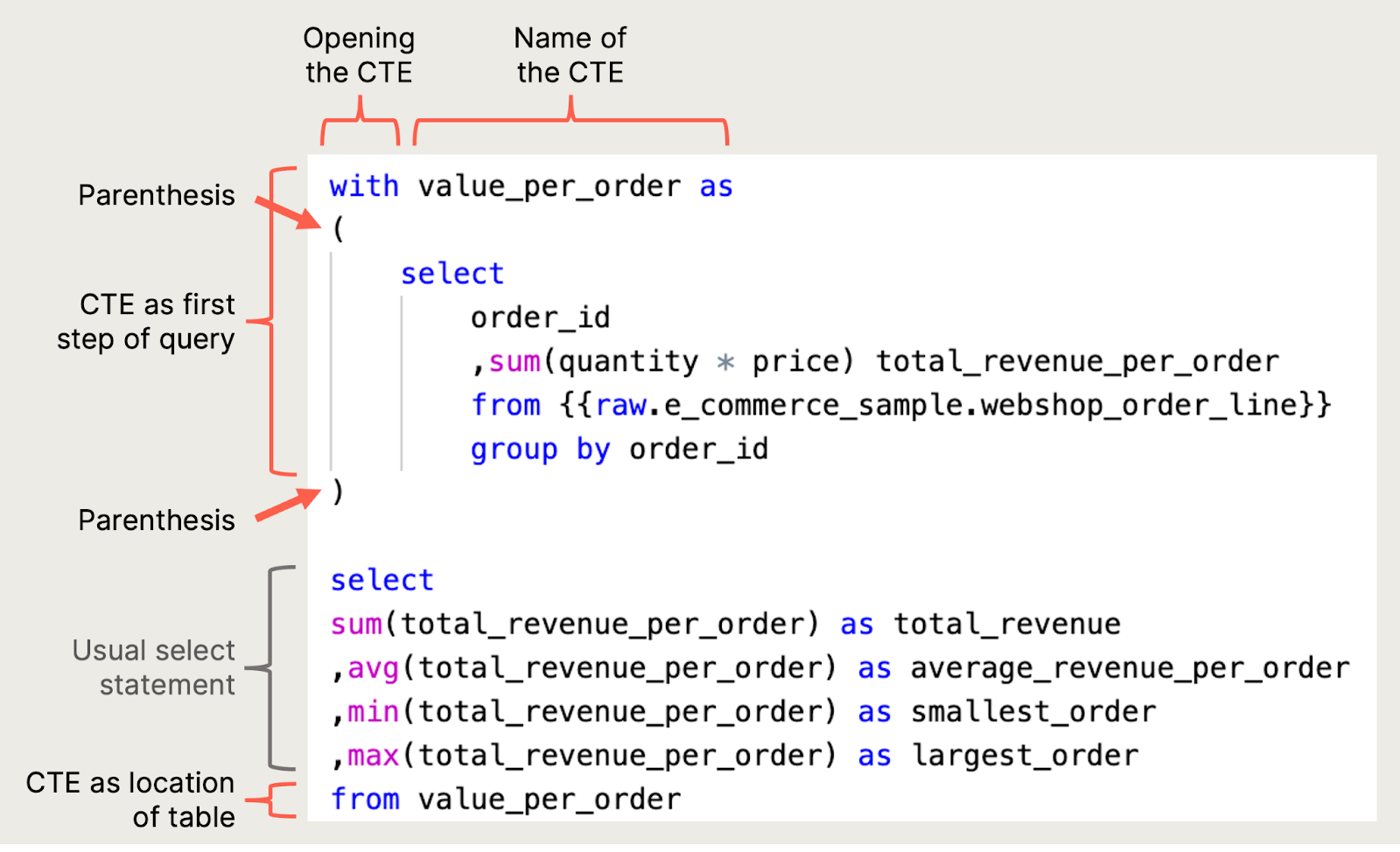
As you can see, the query is now split into two steps. The first one is your CTE and the second is a SELECT statement with some aggregating functions used earlier. But this time the temporary table (the CTE) is referenced in the FROM statement. The CTE is started with a WITH statement followed by the name given to this temporary table, and an AS (.
Inside the parenthesis, the SELECT statement, aggregating functions, and FROM statement work exactly as you’d expect. The CTE ends with a ). After the CTE you can also write the SELECT statement exactly as before, but this time instead of referencing another table in the FROM statement, you simply reference the CTE. Take a closer look at how CTEs are added to queries with another example:
1with
2 value_per_order as (
3 select
4 order_id
5 , sum(quantity * price) total_revenue_per_order
6 from
7 {{raw.e_commerce_sample.webshop_order_line}}
8 group by
9 order_id
10 )
11select
12 *
13from
14 value_per_orderThis example doesn’t make much sense — adding a CTE complicates the query, only to simply SELECT all the columns in the final SELECT statement. There’s no point in using CTEs except if you need to perform analysis in several steps. You could get the same results as with the query above by just writing:
1select
2 order_id
3 , sum(quantity * price) total_revenue_per_order
4from
5 {{raw.e_commerce_sample.webshop_order_line}}
6group by
7 order_id




